This guide will teach you everything you need to know about a keto diet and bodybuilding.
First off, it is possible to build muscle on a ketogenic diet.
You will learn…
How to set up your keto diet.
How to train on a keto diet.
Plus much much more.
Let’s get started…
but first click here => 1
Don't have time to read all 8,000+ words? Download a PDF to read offline at a later time.

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Consistency of the fundamentals
The keto diet and bodybuilding are two words you may not often see thrown in the same sentence
One question I hear most is whether or not you can build muscle while on a keto diet. In short, yes it is possible to add muscle while on a ketogenic diet and I'm here to tell you how.
Trust me, I was there and had those very same questions, but I'm here to share with you that IT IS possible and many individuals are doing so.
When it comes to building muscle, it boils down to about four fundamental principles whether you're on a ketogenic diet or a high carbohydrate diet.
Keto diet bodybuilding fundamentals
A “traditional” bodybuilding regimen typically follows a super high carb high protein and virtually no fat diet, almost opposite of a ketogenic diet.
It's no wonder why there are so many people that question whether or not they can build sufficient muscle on a ketogenic diet.
Again, trust me… I was there! But when it comes down to it, building and/or maintaining muscle comes down to a few fundamental principles:
- TRAINING. Sufficient stimulus and overload
- NUTRITION. Enough calories and protein
- RECOVERY. Rest and quality sleep
- ADVANCED. Supplementation and meal timing
The bodybuilding world filled with all sorts of bro science and overhyped supplements, but when it comes to building muscle, you can't argue with key fundamentals backed by science.
A little forewarning:
First off, there is a strong chance you will not be able to work out with the same intensity as before… INITIALLY. That is, your body hasn't adapted to using fat as fuel or what many refer to as becoming fat adapted or keto-adapted.
Many say this process takes about 3-4 weeks, but from mine and many others personal experiences… it only gets better and better as time goes on.
Eventually, your gym performance will surpass that of when you were on a standard carbohydrate based diet.
With that said, let's get to the fundamental principles for putting on some quality muscle on a ketogenic diet.
Chapter 2: Keto bodybuilding and progressive overload
The most closely associated variables with muscle hypertrophy (growth) are progressively overloading your muscles and increasing your training volume.
Meaning, stressing your muscle over time and performing an adequate amount of volume (done by increasing your reps and/or sets)
Depending on the program, this can occur daily, weekly, monthly, or even over a longer duration of your choosing. The most IMPORTANT concept is that we do MORE over time.
Different progression schemes
The body will adapt to the stress of resistance training with increased fitness, in our case… muscle growth. Of course, the stress must meet a minimum threshold of intensity.
If the stress is not sufficient to overload the body, no adaptation will occur.
FORCE YOUR BODY TO ADAPT AND GROW!
LINEAR LOAD INCREASE
The weight used increases from week to week or session to session generally on the same exercise.
LINEAR REP INCREASES
An increase in the number of repetitions from week to week or session to session generally on the same exercise.
LINEAR SET INCREASES
Increase the number of sets performed from week to week or session to session generally on the same exercise.
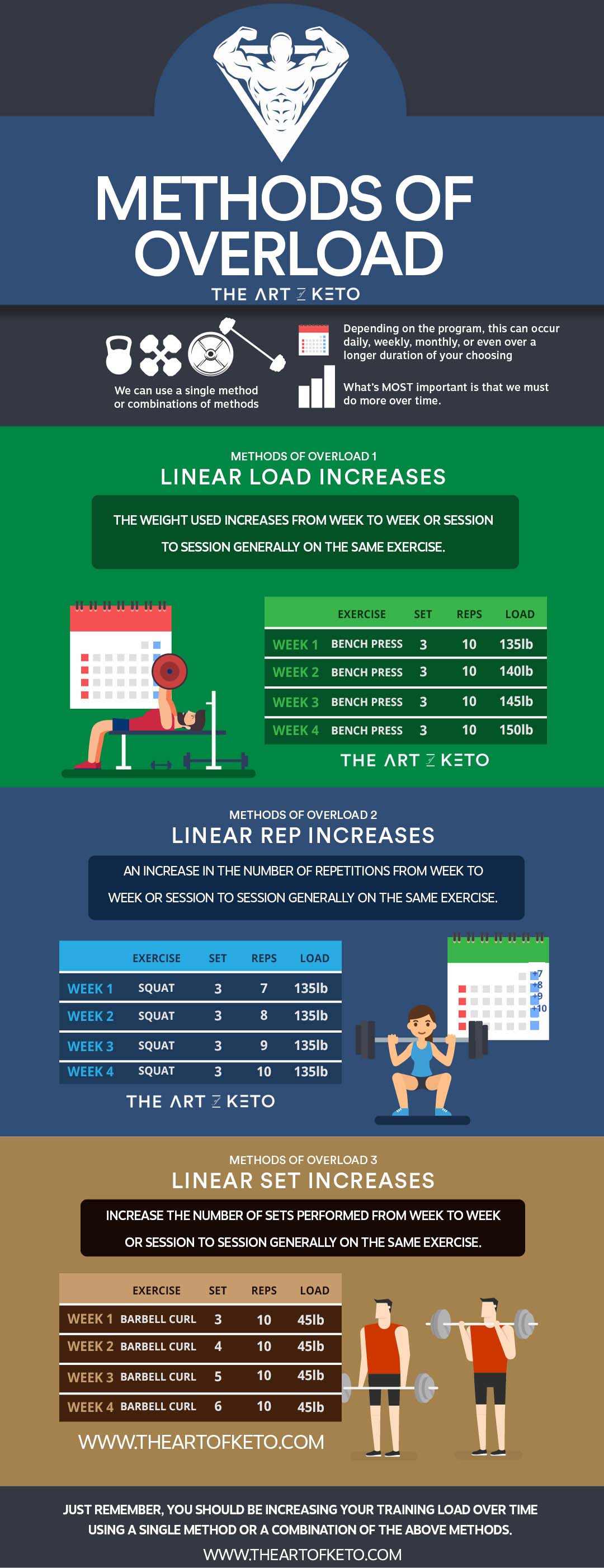
ust remember, you should be increasing your training load over time using a single method or a combination of the above methods.
While strength increases are a useful marker for the effectiveness of your training program, it is not necessarily our primary function when it comes to bodybuilding which is muscle growth.
Just think of strength as a very welcome side effect. Hypertrophy is one component of strength, but not the other way around.
Furthermore, if you are effectively overloading the muscle and generating growth, you'll likely get stronger over time, but a part of that strength increase is also due in part to skill development (becoming more proficient) with the exercise and neurological adaptations.
Nevertheless, an increase in strength is also a useful marker of your training programs effectiveness. 2
Chapter 3: Keto bodybuilding nutrition
Ever heard the phrase “Abs are made in the kitchen?” Well, that's because they are.
Whether you're looking to build muscle or lose fat, your diet is almost always the limiting factor WHATEVER your goal and
That being said…
Keto diet and bodybuilding nutrition: CALORIES
During the first couple weeks of starting a ketogenic diet, it is imperative that an adequate or even increased amount of protein intake is consumed.When switching to a keto diet for bodybuilding, your body has yet to shift to a fat-burning metabolism.
Before the adaptation period of about 3 weeks, small amounts of glucose are still required for your brain and body to function, in turn, your body ends up breaking down its own protein stores to provide that glucose.
Eating enough protein will help prevent muscle loss by supplying the amino acids for gluconeogenesis that would otherwise come from your body protein.
However, once your body has made the shift from using glucose as its primary source of energy to using ketones, the need for gluconeogenesis from protein will also decrease.
In fact, once your body is adapted to using ketones for fuel, the ketones exert a protein sparing effect which makes it great while cutting for the summer or getting shredded for the stage.
In the end, the importance of nutrition is no different on a ketogenic diet vs. a carbohydrate-based one regarding the fundamentals laid out below.
However, the macronutrient breakdown will, of course, differ since we are relying on a different source of energy, fat.
Here is an image to help you visualize the degree of importance when it comes to nutrition and meeting your goals.

How much weight is gained, lost, or maintained comes down to energy balance i.e. your calorie intake.
If you're not sure where to start, head over to our keto macro calculator to get a personalized starting point based on your lifestyle and goals or simply use the “easy” calculation method below to generate a great starting point.

When it comes to bodybuilding, people generally have one of two goals, ok maybe three. You either want to lose fat, gain muscle, or the third… accomplish both at the same time.
The ability to gain muscle while losing fat (caloric deficit) usually comes down to:
- Your current body fat percentage
- How trained you already are
- The size of your caloric deficit
Essentially, the higher your body fat and the less training experience under your belt, the higher the likelihood you will be able to accomplish both, provided you're not HEAVILY restricting your calories.
Changes in your diet, rather than manipulating your training or cardio, should be used to create the energy surplus or deficit you need to put on muscle or drop body fat (for the most part).
It's just easier and more effective to control your energy balance through diet than it is through training, but hey… do what makes you happy.
As the saying goes, “You can't outrun a bad diet.”

For a better understanding of calories, how many you should eat, and best practices check out the article on How many calories should you eat on a ketogenic diet? 3
Keto diet and bodybuilding nutrition: MACROS
To oversimplify things a bit, while calories (energy balance) determines whether weight is gained, lost, or maintained, macronutrients (protein, carbs, and fat) determine whether that change comes from fat or muscle.
If you ever hear the term or see me refer to ‘macros' you're just hearing an abbreviated term for the word macronutrients: carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
Macronutrients will be the biggest difference when it comes to a ketogenic diet and bodybuilding vs. your standard bodybuilding diet since our primary energy source is fat and not carbohydrates.
ONE MACRO TO RULE THEM ALL!
Which leaves us to what I consider the most important macronutrient, PROTEIN aka PROTONS. Protein, contrary to all the keto hearsay, is not a bad thing and is actually quite important.
Protein helps us to recover from our training, it preserves your lean tissue when dieting, helps us repair and grow muscle when bulking, and has the highest satiety effect of the three macronutrients.But what about gluconeogenesis?
What about it?
Technically, gluconeogenesis is happening all the time, but there is this common misconception in the keto community that “a little extra“ protein in the diet will magically turn into
As in, excess protein will be converted to glucose and spike your insulin, therefore, knocking you out of ketosis, but this couldn't be any further from the truth.
Gluconeogenesis is a demand driven process. Meaning, it will only occur if it is absolutely necessary.
Myself, along with MANY others have successfully eaten high protein diets while maintaining a state of ketosis. In fact, the ONLY prerequisite to achieving a state of ketosis is the reduction or lack of carbohydrates , not eating high amounts of fat or eating low amounts of protein.

Mind you, if you are using a ketogenic diet for therapeutic reasons, please do so under the care of a medical professional.
Within the keto community it is quite common for people to stick to specific “percentages,” but this can often lead people to unintentionally under consume protein or over-consume fat.
Guidelines for protein intake should ideally be based on an individual’s lean mass and be given in total grams, rather than as a percentage of total energy intake.
Here's why you want to calculate by grams and NOT percentages.
Since we want to base protein on an individuals lean mass, let's give you an example:
This leaves Bob with 39lbs of fat mass and 156lbs of lean mass.
Per my experience and some of the scientific literature, Bob at the very least should be consuming 156 grams of protein, probably more since he is in a deficit. If Bob was dieting aggressively, say averaging 10 calories per pound of bodyweight based per our EZ calculator, that leaves Bob with 1950 calories.
Now, using traditional “ketogenic percentages,” even at the high end of the protein recommendation, 30% ( which is probably higher than what you'll see even at the HIGH end ) this leaves Bob with 146 grams of protein.
Imagine if Bob was eating even less than 1950 calories, protein intake would be insufficient.
One could argue that ketones are muscle sparing, and they are, but when it comes to protein, too much is better than too little.
HOW MUCH PROTEIN ON A KETOGENIC DIET? READ MORE.

For a better estimate, it's best to calculate protein requirements on lean body mass rather than total body weight. We can calculate lean mass by taking our total weight and subtracting our fat weight.
Protein recommendations are based on lean mass since individuals with more fat will end up with too much protein and leaner individuals end up with too little.
Basically, the more lean mass you have the more protein you require.
If you have no idea of what your body fat is, there are a myriad of testing methods such as body fat calipers, a bodpod, electrical impedance, or a DEXA scan.
Either way, all methods tend to have inaccuracies and inconsistencies so the purpose of having it done is to have a general starting point.
If you prefer, you can use the image on our keto calculator page to guesstimate your body fat and also calculate your calories and macros based on your preferences and goals. 4
Another, rather simple, method is to eat 1 gram of protein per pound of DESIRED bodyweight. Meaning, if you were 180 pounds but wanted to cut down to 150 then you would simply eat 150 grams of protein per day.
Other great reads on the other two macros right below:
How many carbohydrates on a ketogenic diet?
How much fat on a ketogenic diet?
Keto diet and bodybuilding nutrition: MICRONUTRIENTS
In short, these are your vitamins and minerals. If you are following a diet rich in whole foods and not solely relying on processed meats or fast food you may more or less have this covered on a ketogenic diet.
Long-term micronutrient deficiencies will eventually impact your health and hamper your bodybuilding efforts.
BUT WHAT ABOUT FIBER?
Depending on which side of the keto fence you land on, this may leave you with some fiber or none at all.
With the rise of the carnivore diet or even the keto carnivore diet, new research is emerging questioning the role of dietary fiber or if it is even required at all to live a happy and healthy life.
Moral of the story, we might not need as much fiber as we have been led to… especially if utilizing a ketogenic diet for bodybuilding.
CAN I JUST TAKE A MULTIVITAMIN?
A multivitamin isn’t a substitute for a poor diet, but it can be insurance on a good one. Those in a calorie deficit have a higher risk of micronutrient deficiencies since their overall intake is less and may benefit from supplementation. 5
Keto diet and bodybuilding nutrition: NUTRIENT TIMING
To define nutrient timing simply, nutrient timing refers to eating specific macros (protein, carbs, or fats) in specific amounts and at specific times (such as before, during, or after exercise, before bed, you get the picture)
Trust me, I've done it all… everything from eating every 2 hours to downing a 4:1 carb to protein shake IMMEDIATELY post-workout, to eating my nightly cottage cheese, and even going as far as having a protein shake ready for when I woke up in the middle of the night.
Every fad, protocol, and bodybuilding folklore has been tested at some point.
As a whole, I've seen the shift from recommendations of eating every 2-3 hours throughout the day to everyone jumping into intermittent fasting and eating only one or two meals per day.
The best answer I can give you regarding meal frequency is that it likely falls somewhere in between one and five meals a day in terms of what is “optimal.”
At a certain point, you're seeing very marginal increases. For the recreational bodybuilder or those who are just trying to look and feel better, I don't believe it matters a great deal.
WHAT ABOUT PRE OR POST WORKOUT NUTRITION?
For years, we all used to believe in the “post-workout anabolic window.” Bodybuilders everywhere were rushing to chug down their protein and carb shakes within 30 – 45 minutes of finishing their workouts.
Well, hate to burst your bubble… but the “anabolic window” is actually a whole lot longer than we used to believe. In fact, muscle protein synthesis is elevated as long as 48 hours after a bout of heavy resistance training.
Recent data suggests that the total amount of protein and calories you eat, over the course of the entire day, is arguably more important for body composition and performance than worrying about nutrient timing.6
Keto diet and bodybuilding nutrition: SUPPLEMENTS
If everything else above is in order, supplements can benefit a good nutrition plan, but they cannot make up for a poor one.
Most people skip directly to this section, because the first thing they want to know is what are the best supplements for keto.
When it comes to a ketogenic diet, the only one I believe to be essential are electrolytes (sodium, potassium, and magnesium).
When everything else above is dialed in, you don't need an extensive supplement list. This is why supplements are at the top of the pyramid and really shouldn't be considered until you have your training, calories, and macros in order.
There are very few supplements with strong evidence to support their effectiveness. Unfortunately, when it comes to most supplements most of them are all talk but here are a few that have deemed themselves worthy of being recommended.Here are the ones I do recommend along with the brands I use and trust due to purity of ingredients.
CAFFEINE
Shown multiple times over to aid in fat loss, gym performance, appetite suppression, and if you're drinking it (i.e. coffee) filled with plenty of antioxidants.
Depending on your sensitivity, I would recommend between 100mg and 200mg 30 minutes to an hour before your workout. Just be mindful of your intake if you workout close to bed since caffeine carries a half-life of 5 to 6 hours.
A 16oz cup of coffee carries about 200mg so that should do the trick.
Another study shows that maybe even higher doses ~3-6mg/kg is required to see any kind of performance benefits.7
- Recommended: Caffeine Tablets
CREATINE
Possibly one of the only well tested, tried, and true supplements.
Creatines benefits expand outside of just performance which makes it one of my most recommended supplements. It is indeed the number one supplements in my opinion for improving your gym performance.
I recommend a dose of 3g – 5g of creatine per day and with creatine being so cheap, why not? You can buy nearly a years supply for $20.
- Recommended creatine: Bulk supplements creatine
- Recommended creatine: Musclefeast creapure
Foods rich in creatine include beef, salmon, and tuna.
FISH OIL
I recommend eating plenty of omega-3 rich foods and possibly even supplementing in most cases. The typical diet contains about 10x more omega-6s than omega-3s.
This is why it's important to pay attention to food quality and sticking to whole and unprocessed foods when possible. Many experts believe we should be closer to a ratio of 2:1 (omega-6:omega-3) for optimal health.
If you're mindful of your food choices on a ketogenic diet you should be closer to the average than most people already. Personally, I aim for anywhere between 1,000 and 2,000 milligrams of combined EPA/DHA day.
- Recommended fish oil: Fish oil pills
- Recommended fish oil: Fish oil liquid
Foods rich in Omega-3 include fatty fish, ( mackerel, wild caught salmon, sardines ) walnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, and pasture-raised egg yolks.
VITAMIN D3
Vitamin D is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight, so If you find yourself in an area with very little or don't get out much then I would highly recommend between 1,000 – 6,000 IU per day.
- Recommended Vitamind D: Vitamin D3 Soft Gels
Foods rich in Vitamin D include fatty fish, ( mackerel, wild caught salmon, sardines ) beef liver, and egg yolks.
WHEY / CASEIN PROTEIN
First off, there's nothing magical about whey or casein protein, but if you're having trouble hitting your protein intake then supplementing can make a difference. Just look at protein powders as just foods in powdered form and nothing more.
- Recommended protein powder: Grass-Fed Whey isolate
- Recommended protein powder: Grass-Fed Casein
- Recommended protein powder: Vegan protein
KETONE SALTS
Great for a boost of energy / pre-workout or while making the transition to a ketogenic diet. Ketone salts or exogenous BHB supplements can supply you with a quick burst of energy.
- Recommended Ketone Salts: Perfect Keto Exogenous Ketones
MCT OIL
Medium Chain Triglycerides are digested easily and sent directly to your liver, where they can be quickly converted to ketones because they require fewer steps to be metabolized in your cells.
Personally, I'll take about a tbsp (15g) in my pre-workout cocktail. If new to MCT oil I would suggest starting with about 5g and work your way up in dose. MCT oil has been known to give people the case of disaster pants.
- Recommended MCT (C8 Oil): C8 MCT Oil
- Recommended MCT Powder: Perfect Keto MCT Oil Powder
- Recommended MCT Oil: Viva Naturals MCT Oil
Chapter 4: Keto diet bodybuilding recovery
Recovery from muscle breakdown is an often overlooked piece in this muscle building and fat loss puzzle.
After all, the better you can recover from workouts, the more frequently you can train, and training frequency does play a major key in hypertrophy (muscle gain).
I’m not advocating that hitting your chest every day is going to make it grow exponentially, but there is research to suggest that training a body part 2-3x per week seems to be more optimal if muscle growth is your goal.
With that said, recovery can be boiled down to some key principles.
- Proper nutrition. Giving your body the fuel it needs.
- Plenty of rest. Plenty of sleep, taking days off, and planned
deloads . - Managing stress. Not much to add here.
Keto bodybuilding recovery: NUTRITION
Proper nutrition
Since we covered nutrition earlier, we won’t go into too much depth here, but a big part of recovery comes down to how much and what foods you put into your body.
You want your body to have the resources it needs to repair itself whether you’re looking to lose fat or pack on some muscle.
I can go on and on about food quality, but you either believe that food quality matters or you don’t so I’ll leave you with this tidbit, everything you put in your mouth either helps you or hurts you.
Now, when it comes to nutrition and recovery, you want to be following the guidelines we laid out above to first determine how many calories you should be eating and then following that up with making sure you are eating a sufficient amount of protein.
To rehash your memory here is the order of importance.
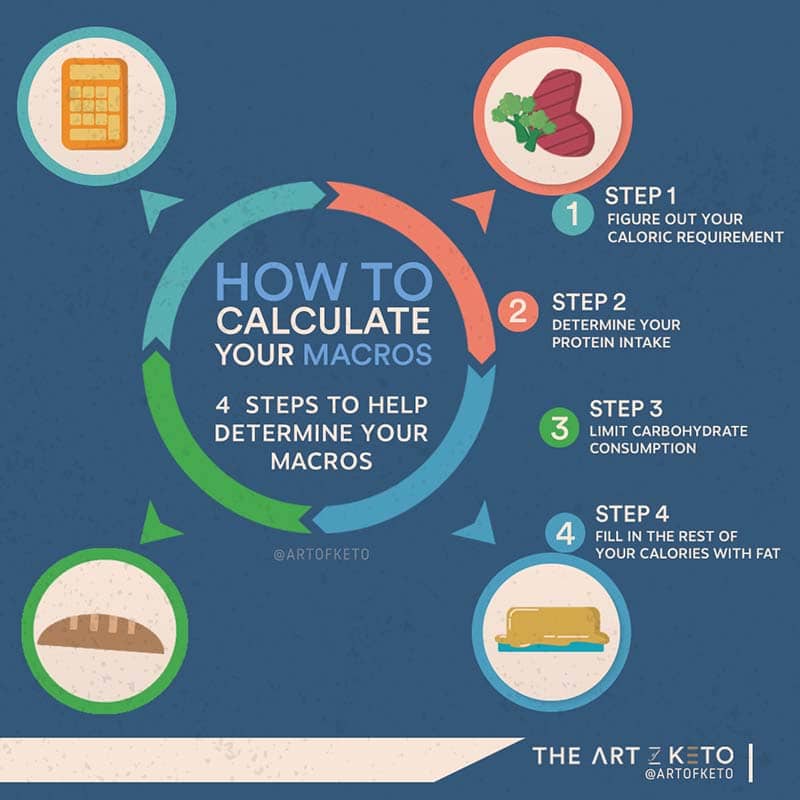
- Determine your calorie requirements (yes, calories still matter)
- Eat an adequate amount of protein
- Restrict your carbohydrates
- Fill in the remaining calories with fat
If muscle gain is a priority
An extra 250-500 calories
Muscle gain expectations
Regarding muscle growth, your level of training and even your genetics play a massive part in what determines muscle growth potential.
The more advanced in training age you are, the slower it'll likely be to pack on some muscle. Below is a rough breakdown of the rate of growth you can expect based on your training age:

If fat loss is a priority
How fast you want to lose body fat is determined by your caloric deficit. If we take the number of 3500 calories, the amount of calories in 1 pound of fat, we can assume that if we subtract 500 calories per day over the course of a week (500 calories x 7 days) that we would lose around 1 pound per week.
Therefore, if we were to increase our calorie deficit to 1000 calories per day, we could assume about a 2-pound decrease per week.
These are just estimates and don’t always work out this way since a lot of factors are at play, but in general, these principles do apply.
Fat loss expectations
Fat-loss tends to be proportional to a person's body fat percentage rather than total body weight. In general, the higher your starting body fat, the more aggressive you can be.
The below recommendations should be a realistic expectation of fat loss while also preserving muscle mass using a keto diet for cutting: 9
Keto bodybuilding recovery: REST
All about rest
Rest comes down to three parts:
- Days off from training
- Deloading (strategic periods of less volume and intensity)
- Sleep. Many individuals undervalue the importance of getting a sufficient amount of rest and end up burned out or spinning their wheels wondering why they aren’t seeing any progress in the gym.
1. Days off from training
As a culture, we tend to think the harder and longer we go the “bigger the gains” and this is true… to a certain extent.
Up to a certain point, the more is
Your body doesn’t grow while you’re in the gym. If you’re not taking time away from the gym, your body doesn’t have time to adapt by becoming bigger and stronger than it was before.
2. Strategic deloads
Just as in life or business, training should also have a period of time where you reduce the intensity and volume.
Much like taking a vacation from work, by taking our foot off the gas for a brief period, it allows us to dissipate any fatigue and come back with a renewed sense of purpose and energy.
A deload may sound counterproductive, but if you want to make the best muscle and strength progress, you shouldn’t be training hard all the time.Or best put, you cannot. After some time, residual fatigue accumulates, and performance ends up taking a dip and worse performance = fewer gains. Now, what once was your 100% may now only be 85%.
Can you still make progress without a deload? Sure, but you could make better progress by incorporating these periods of less intensity and volume, and that’s where a deload comes in.
Again, Why should you deload?
- Dissipate fatigue
- Mental rejuvenation
- Time to heal any possible injuries
- Allows a progressive system to ensure overloading
Picture a deload as walking up four flights of stairs, but we stop for a short rest on the fourth floor. We stop just long enough so that we may catch our breath and regain enough energy to continue another four flights of stairs before rinse and
How to implement a deload
In order to deload, all we are doing is reducing our intensity and volume to reduce the accumulated fatigue from weeks of hard training while maintaining our fitness.
In practice, you should not be going so hard as to cause more fatigue and muscle damage. At the same time, you should not be going too easy that you lose substantial fitness.
Just
For this purpose, I generally schedule a deload every 4-6 weeks where I reduce the load (weight) on every exercise by about 5% and cut my volume by about 25 – 50%
For example:
If in my 4th week of training after coming off a previous deload I was squatting 315lbs for four sets of 10 reps. During my 5th week (deload week) I would do the below:
315 x .05 = 300lbs (we’ll just round for simplicity sake)
4 / 2 = 2 sets
10 / 2 = 5 reps
Essentially, I would do 300lbs for 2 sets of 5 reps on my leg day for squats during my deload week and then I would apply this same load and volume decrease on every exercise during my deload week.
Again, the main goal is to allow us to continue progressing with maximum performance. It may suck to take it a bit easier every now and then, but the benefits far outweigh the negatives IMO.
Done correctly, you should be coming off that week stronger, feeling better, and even more excited to hit the weights hard.
3. Sleep
We all know that the body needs sleep, after all… sooner or later we all get tired. But how much sleep we need is difficult to determine because, like many other things, it depends on individual differences.
Besides, who doesn’t like sleep?
What most people don’t realize Is that sleep and muscle growth, and even fat loss, go hand in hand. During our workouts and even day to day life, we create microscopic tears within our muscle on a cellular level.
It’s these tears that repair and rebuild resulting in muscle growth. The biggest factors in how well our muscles repair after training are our sleep and our nutrition.
While not always possible, you should be aiming for anywhere from 8 to 10 hours of sleep every night. It is when we sleep that our body creates spikes in larger amounts of vital hormones for muscle repair and growth such as HGH, testosterone, and melatonin.
Moral of the story, get some shuteye.
Keto bodybuilding recovery: STRESS LESS
DESTRESS
There’s an often overlooked aspect to muscle gain or fat loss, and that’s stress. That’s because stress physiology can cascade down and effect virtually every other system in our body including the immune system, endocrine system, neurological system, and gastrointestinal system.
If you’re frustrated and know you may be doing everything right and still not seeing any progress, stress may be one part of your life you may need to take a good hard look at.
Lots of chemical responses occur during periods of stress including:
- Rising levels of cortisol secretion. Cortisol isn’t bad in and of itself, but when it spikes and stays elevated for prolonged periods this may hamper your progress in the gym. Elevated levels of cortisol may negatively impact blood sugar levels, digestion, metabolism, fat storage, and the immune system.
- Hunger and cravings increase. FOR SUGAR! Yepp, quite counterproductive for those looking at bodybuilding on keto as an alternative to the mainstream. Hormonal changes in the body can be the cause for that Ben and Jerrys craving.
- Thyroid gland slows production. One of the essential hormones needed for metabolism. It may be one reason why you may spinning your wheels in the gym and sticking to your diet and not seeing the scale budge in the right direction.
- Increase catabolism. Breaking down of muscle to use as energy while increasing fat stores… quite the opposite of what we’re looking to accomplish.

Adequate sleep, calories, and attention to recovery as we’ve gone over earlier in the article are three of the biggest factors that we have control over on a daily basis.
In addition, supplements like ashwagandha and chaga mushrooms have been shown to aid in adaptation to stress.
Recommended ashwagandha: KSM-66
Recommended chaga mushroom: Chaga powder
Also, take time to relax! Go for a nice walk outside and soak up the sun, get a massage, watch a good movie, and my personal go to. MEDITATE.
I was never into meditation and was even a bit skeptical at first, but having incorporated meditation into my daily routine, the results speak for themselves.
In the end, do something you enjoy and helps you relax, feel happy, and most importantly stress less and unwind. 10
Recovery is an often overlooked aspect in peoples fat loss or muscle gain goals. Some tips for helping manage recovery:
- Get adequate sleep (8-10 hours)
- Proper nutrition (sufficient calories and protein)
- Taking days off from the gym and planned periods of lower intensity
- Managing stress by finding things that relax you and give you joy
Chapter 5: Keto bodybuilding concerns
Many of the same principles apply to gaining muscle and losing fat on a ketogenic diet as they do on your standard carbohydrate based diet.However, there are some common concerns when it comes to bodybuilding on keto due to a lack of understanding and frankly a lot of misinformation and hearsay.
While not everything is fully understood in the realm of a keto diet and bodybuilding, research and anecdotal evidence is beginning to emerge at an increasing rate.
Water loss on a ketogenic diet
It’s well established that low carbohydrate diets, especially a ketogenic diet, cause rapid loss of water in the first few days. Reason being, three grams of water is stored for every gram of stored carbohydrate.
Additionally, ketones appear to have a diuretic effect themselves causing the excretion of water and electrolytes.
With a water loss of only 2% of your body weight, physical performance will be impaired, and with a 2.8% water loss, your cognitive functions begin to be impaired as well.
This amount of water loss can easily occur during the first week of a ketogenic diet as the body sheds water and sodium due to the reasons explained above.
If not mindful of your water and electrolyte intake especially during the first week of transitioning to a ketogenic diet, you may experience what is commonly referred to as the “keto flu.”
Basically NOT GOOD.
To diminish or even avoid these symptoms altogether, make sure you are drinking plenty of water and increasing your electrolytes. I usually suggest people aim for close to a gallon of water a day and between 4,000mg – 6,000mg of sodium.
I suggest people liberally salt their meals and possibly even dilute some salt in their water throughout the day to ensure adequate sodium intake.
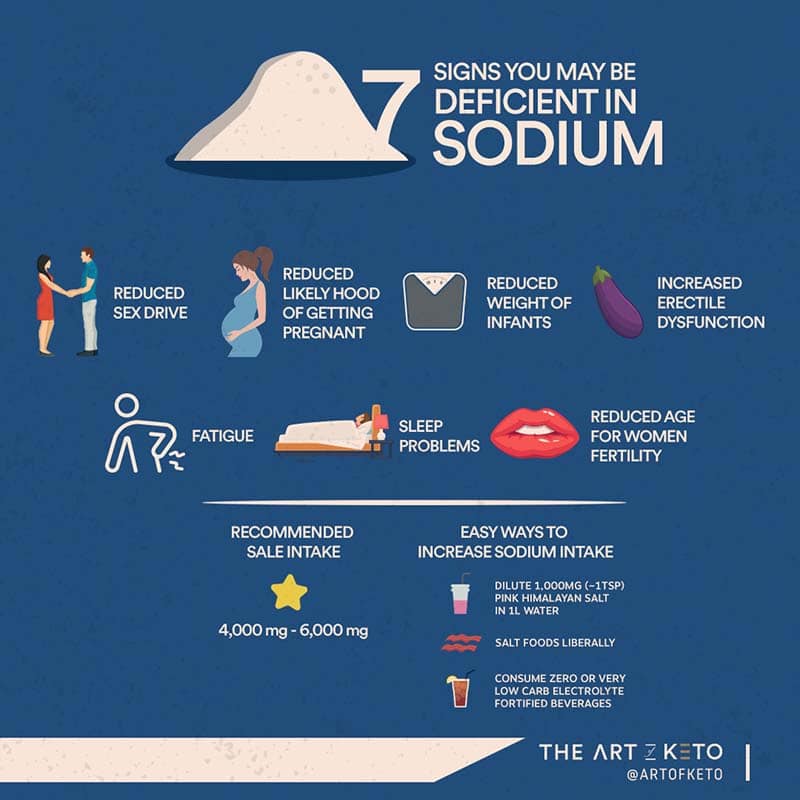
TAKE HOME
Ketogenic diets cause a loss of water due to carbohydrate restriction and the fact that ketones exert a diuretic effect causing a loss of water and electrolytes.
To counteract the performance and cognitive decline that may happen you should increase your water intake (around 1 gallon per day) and electrolytes, especially sodium (4,000mg – 7,000mg).
Glycogen replenishment without carbohydrates
Often, a concern about a ketogenic diet for bodybuilding leads one to ask how glycogen is replenished.
The whole idea behind replenishing glycogen immediately following a workout was to set our bodies up for the next workout and switch off catabolism (bad) and switch on anabolism (good).
To break it down, we are trying to accomplish:
- Replenished glycogen I.e. replenish energy stores
- Decrease protein breakdown i.e. build bigger muscles
- Increase protein synthesis i.e. repair damage from our workout
This is why you’ll often recommend eating carbohydrates post workout or ingesting a sugar-filled protein shake immediately post-workout. I used to do it, I’m sure you may have or may still be doing it, but I’m here to let you know there’s no need.
You’d have to train a muscle twice daily with a volume you could not possibly recover from in order to require carbs to replenish your glycogen in time for the next training session.
It’s been shown that when ample protein is ingested, carbs do not have any additive effect on protein balance.
Even with very minimal amounts of carbohydrates, as with those trying to use a keto diet for bodybuilding purposes, your body has more than enough to maintain a proper bodybuilding routine.
Research by Volek found that long-term ketogenic dieters not only have similar pre-exercise levels of glycogen but also deplete glycogen slower AND replete glycogen at a similar rate compared to long-term carbohydrate-adapted athletes.
This is likely an adaptation that occurs following longer adherence to the diet and becoming fully keto-adapted.
So, do we need glycogen and if so, how is glycogen replnished without carbohydrates?
Glad you asked…
Yes… your body does use glycogen when lifting, but this glycogen is already in your muscles.
What you eat right before your workout has very little to do with what your performance will be like, it’s more about what you already had inside your muscle. 11
Even high levels of bodybuilding (LOTS of
So how is glycogen replenished then?
The science behind this is explained via the Cori Cycle. The Cori Cycle provides the body with important pathways to maintain adequate muscle glycogen levels without glucose from the diet.
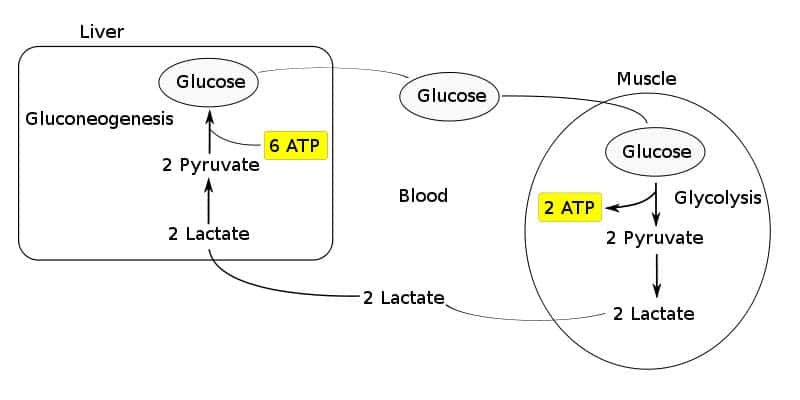
Glycogen can come from the conversion of lactate, a by-product of glycogen breakdown in the muscle, to glucose in the liver. This newly made glucose is released into the bloodstream and stored again in the muscle as glycogen.
As you see, low carbohydrate dieting isn’t the “performance killer” that people make it out to be. Therefore, If you’re looking at bodybuilding and strength training, the keto diet is not an issue.
Chapter 6: Keto diet and bodybuilding advanced strategies
Okay, so we gave you a breakdown of the three primary macronutrients in our ultimate keto diet food list. We even gave you our best recommendations for beverages, but what about supplements?
As this is primarily keto food list, we'll keep this section brief with some keto supplement recommendations we frequently get asked about.
Carbs as a tool to improve exercise performance
If you are an already lean individual or have noticed your performance in the gym still suffering, even after adapting to a ketogenic diet, you may benefit from strategically increasing carbs around your workouts.
The two main methods of strategically using carbs are known as a targeted ketogenic diet (TKD) and a cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD).
Having experimented with both a TKD and CKD, I much rather have people utilize the former rather than the latter.
The TKD is a much more simple strategy to implement that doesn’t involve complicated workouts and shifting your body out of ketosis for prolonged periods of time.
However, there is a time and place for everything. There are plenty of successful bodybuilders that utilize a cyclical approach to a ketogenic diet and make amazing progress.
The Targeted Ketogenic Diet
The TKD is a compromise to staying in ketosis ala the standard ketogenic diet, but instead, we interrupt ketosis for a short period of time by strategically implementing carbohydrates before and/or after our workout.
While studies giving carbs prior to resistance training have not found an increase in performance, anecdotal evidence from myself and many others have noticed improved strength and endurance from as little as 5-10g of carbohydrates right before working out.
Research also suggests that carbohydrates consumed before or after exercise should not negatively affect ketosis. Though, if you happen to drop out for a short period do not fret, you’ll likely jump right back in within a couple of hours. 12
Chapter 7: My top 5 tips for bodybuilding on keto
I'll be the first one to say that what works for one person may not work for the next.
If you decide on a keto diet and bodybuilding as your plan of attack, the best thing you can do is EXPERIMENT.
Every day is a chance to learn about yourself, your body, and make adjustments based on real-world results.
I believe a ketogenic approach is a great compromise between optimal health and aesthetics.
That said, I guess that makes it 6 tips.
🙂
Tip #1 Consistency is the name of the game. Muscle gain is a slow process and while
Tip #2 Stick with a standard ketogenic diet for at least 3-4 weeks before deciding you want to strategically implement carbohydrates for performance.
It takes your body at least 3-4 weeks to become accustomed to utilizing free fatty acids and ketones as its primary fuel source.
Tip #3 Supplement sodium pre-workout. I take 1-2g (.5-1tsp salt) in my pre-workout cocktail. This allows me to push harder and also get those “pumps” we all seek at the gym.
Tip #4 If you want to optimize muscle protein synthesis, it might not hurt to spread out your protein between 3-4 meals.
Tip #5 Use good form and a full range of motion on all your lifts even if that means lowering the weight.
Recent studies suggest that a full range of motion led to more muscle activation and growth even with lighter loads than the participants who used heavier loads with
Chapter 8: Keto diet plan for bodybuilding and closing thoughts
All good things must come to an end, but before I go, I want to leave you with some final tips and examples to get you on your way.
Sample keto diet for bodybuilding
First off, there are no magical keto diet bodybuilding macros that I am about to present to you. What follows is based on the principles outlined above and using our EZ calculation method for determining calorie intake.
Muscle gain
Based on a 180lb male at 10% body fat looking to put on muscle.
- 180 POUNDS X .10% = 162lbs of LBM and 18lbs of FAT MASS
- TOTAL CALORIES = 180 x 18 = 3240 CALORIES
- PROTEIN = 162 (lbm) X 1g/LBM = 162g PROTEIN = 648 CALORIES
- CARBS = < 30 = 120 CALORIES
- FAT = (3240 – PROTEIN CALORIES – CARB CALORIES) / 9 3240 – 648 – 120 = 2480 CALORIES / 9 (9 CALORIES PER GRAM OF FAT)
TOTALS 3240 CALORIES 162g PROTEIN 30g CARBS 276g FAT
SAMPLE KETO DIET FOR BODYBUILDING BREAKDOWN
TIME:BREAKDOWN
0600: PRE-WORKOUT COCKTAIL (CREATINE, SODIUM, CAFFEINE, 10g MCT OIL, 20g WHEY PROTEIN)
0630 – 0730: TRAINING
0830: MEAL 1 35g protein 10g carbs 66g fat
1230: MEAL 2 35g protein 5g carbs 66g fat
1630: MEAL 3 35g protein 5g carbs 66g fat
1830: MEAL 4 35g protein 10g carbs 66g fat
Fat loss
Based on a 180lb male at 20% body fat looking to drop body fat.
- 180 POUNDS X .20% = 144lbs of LBM and 36lbs of FAT MASS
- TOTAL CALORIES = 180 X 13 = 2340 CALORIES
- PROTEIN = 144(lbm) x 1g/LBM = 144g PROTEIN = 576 CALORIES
- CARBS = <30 = 120 CALORIES
- FAT = (2340 – PROTEIN CALORIES – CARB CALORIES) / 9 2340 – 576 – 120 = 1644 CALORIES / 9 (9 CALORIES PER GRAM OF FAT)
TOTALS 2340 CALORIES 144g PROTEIN 30g CARBS 183g FAT
1000: MEAL 1 48g protein 10g carbs 57g fat
1400: MEAL 2 48g protein 10g carbs 57g fat
1700: PRE-WORKOUT COCKTAIL (CREATINE, SODIUM, CAFFEINE, 10g MCT OIL)
1730 – 1830: WORKOUT
1930: MEAL 3 48g protein 10g carbs 57g fat
These are just examples of how one can calculate their calorie needs macro needs.
Using the easy calculation above might serve as a great starting point for some and be way off for others. It’s best to track on a weekly basis and make adjustments based on results or lack thereof.
Closing words
Ultimately, fat loss or muscle gain boils down to expending more calories than is consumed or eating more calories than is expended. Some individuals have difficulty restricting calories on a high-carbohydrate diet. GUILTY.
If lowering carbohydrates and increasing dietary fat increases satiety, and makes it easier to control calories, then a ketogenic diet for bodybuilding may be a better dietary choice for you
(Not to mention many of the health benefits myself and others experience on a ketogenic diet).

The keto diet is very appetite suppressing, this is one of the most significant benefits because it becomes easy to drop fat (by eating less than your body burns).
Fat tends to slow digestion, meaning that food stays in the stomach longer, providing a sense of fullness.
The same has been shown to for protein. Additionally, protein stimulates the release of the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) which is thought to help regulate appetite.
In general, individuals who begin a ketogenic diet without paying attention to calorie, protein, or fat levels will automatically lower their caloric intake below maintenance.
Therefore, if muscle gain is your goal, it may be useful for you to track your calories and macros. Otherwise, the resulting caloric deficit will result in weight/fat loss.
Putting it all together
Done correctly, a ketogenic diet with bodybuilding is an effective way to achieve not only health but your body composition goals.
IT IS POSSIBLE!
TO OPTIMIZE YOUR DIET FOR MUSCLE GAIN:
- Eat a calorie surplus of 250 – 500 calories per day. The aim is to increase bodyweight by .5 to 1 pound a week. Stick to the lower weight gain range the more trained you are.
- Keep protein intake between .8g – 1g per pound of lean body mass
- Some studies show benefits of splitting protein between 3 – 4 meals
TO MAXIMIZE YOUR DIET FOR FAT LOSS:
- I usually suggest a deficit of 10 – 20% below maintenance to ensure muscle is preserved. Heavier individuals with more body fat may be able to get away with bigger deficits. Aim to decrease bodyweight 1 to 2 pounds per week.
- Keep protein intake between 1 – 1.2g per pound of lean body mass and create your calorie deficit by reducing your fat intake.
AND IN SHORT:
- Progressively overload your muscles providing the stimulus needed to grow.
- Consume enough calories and protein based on your goal.
- Get adequate sleep
These are the main principles to muscle growth or fat loss regardless of diet. However, you can further optimize your health and bodybuilding results by including some of the following:
- Supplement with tried and true supplements backed by strong evidence such as caffeine and creatine.
- Include MCT Oil and/or Exogenous ketones like Perfect Keto BHB
- Use carbohydrates as a tool to improve performance by following a targeted ketogenic diet as described above.
Are you currently on a ketogenic diet with the goal of adding muscle to your frame?
Any questions? Feel free to drop them down below.
Enjoyed the guide? Share it using any of the buttons above, I would greatly appreciate it.

