Some people question whether or not you can put on any muscle while following a low-carb or ketogenic diet. Not only have I cut on keto, but I’ve successfully bulked up and added muscle to my frame while on a ketogenic diet. For whatever reason, there's a lot of misconception about how to bulk on keto and gain quality muscle.
While bulking on a keto diet may not be an ideal situation, it can be done. To gain muscle on keto, eating sufficient amounts of protein, and providing the necessary muscular stimulus is required. Eating in a caloric surplus will provide an ideal environment for muscle gain.
In this article, I’ll go over how to bulk on keto WITHOUT getting fat, how to calculate your keto bulking macros, and even a few examples of keto bulking meals.

How To Bulk On Keto
First, let’s address the elephant in the room 1 You certainly CAN build muscle on a ketogenic diet. I and plenty of others have managed to do so.
By the time you’re done reading this, hopefully, you will have the knowledge and confidence to go out and have a successful keto bulk as well. Now, this isn’t an article meant to tell you whether or not keto is the best or most optimal way to bulk, but rather how to build muscle on keto effectively.
Building Muscle On Keto
Building muscle on keto can be broken down to a few factors, most notably, your total energy (calorie) intake, having sufficient protein, and progressive overload via resistance training.
First and foremost, the most optimal training and nutrition won’t mean a thing if you can’t stick to it. Learn to pick and choose your battles to avoid feeling burned out and making your approach unsustainable.
- Adherence
- Energy balance
- Macronutrients
- Micronutrients
- Nutrient timing
- Supplements

Keto Adaptation Period
If you’re transitioning to a ketogenic diet, it will take three to four weeks on average for your body and brain to adjust utilizing free fatty acids (FFA) and ketones as its primary fuel source. While the transition period affects everyone differently, you may notice a decrease in performance during this time.
The worst thing you could do during this period is to throw in the towel on your keto bulk. Rest assured, your performance and strength in the gym should return and likely increase after this period if it decreases at all.
Another thing to note, during the first few weeks of a ketogenic diet, protein requirements should be increased due to the increased rate of gluconeogenesis.2
One hundred fifty grams of protein should be the minimum amount of protein during the adaptation-phase to achieve nitrogen balance. This amount will serve to supply enough amino acids and prevent muscle breakdown during the keto-adaptation phase.3
How Many Calories To Bulk On Keto?
There’s often a misconception of how many calories one should consume to gain weight, more importantly, lean mass. After all, your goal isn’t simply to gain weight; it’s to put on muscle. Once you hit a specified rate of gain, a disproportionate of it will be fat.
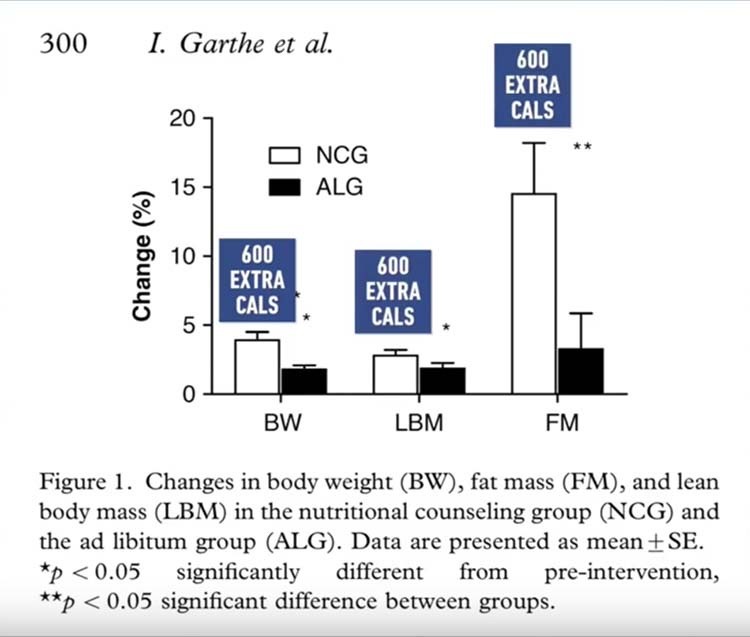
A study by Garthe et al. on elite performance athletes led the non-control group to gain ~5x more fat mass than the control-group eating ad-libitum.4 On average, the calorie intake of the non-control group was only ~500-600 calories more than the control group. Yet, they didn't gain any notable amount of lean body mass over the control group, only a significant amount of fat mass.5
So How Fast Should You Bulk?
Some key factors usually dictate the rate at which you can gain muscle:
- Current body composition 6
- Training experience 7
- Detrainee 8
Current body composition
Before getting started, as a general rule, I recommend men over 18% body fat and women over 28% body fat to first begin with a cutting phase before trying to bulk on keto. I say to cut first because doing so will set you up for long term success allowing more calories to be partitioned towards muscle versus fat when you do decide to do your keto bulk.
Additionally, losing some fat can offer a drastic change to your appearance, often making you look more muscular. After all, the ultimate goal is to look more jacked. If you’re interested in the BEST way to lose those love handles on keto, I wrote about that in detail, 12,000+ words, to be exact.
These aren’t black and white rules, but it’s an excellent place to start, especially if you’re wondering if you’re on the fence of whether to cut or bulk first.
Training experience
In short, the more training experience you have, the closer you’ll likely be to your natural genetic limit. As a consequence, the more advanced you are in the weight room, the more difficult it will be for you to gain lean mass.
Conversely, if you are new to weight training, you should theoretically be able to gain muscle much faster, possibly while simultaneously losing fat (i.e., body recomposition).
What’s this mean for you?
If you’re a beginner, you can use a more substantial caloric surplus with less risk of gaining fat. When you’re advanced, a large caloric surplus will lead to more fat gain rather than muscle, since you are more “resistant” to muscle gain.
Categorizing training experience for your bulk 9
- Beginner: 0-2 years of lifting on average.
- Intermediate: 2-5 years of training on average.
- Advanced: 5+ years of serious lifting on average.
Detrainee
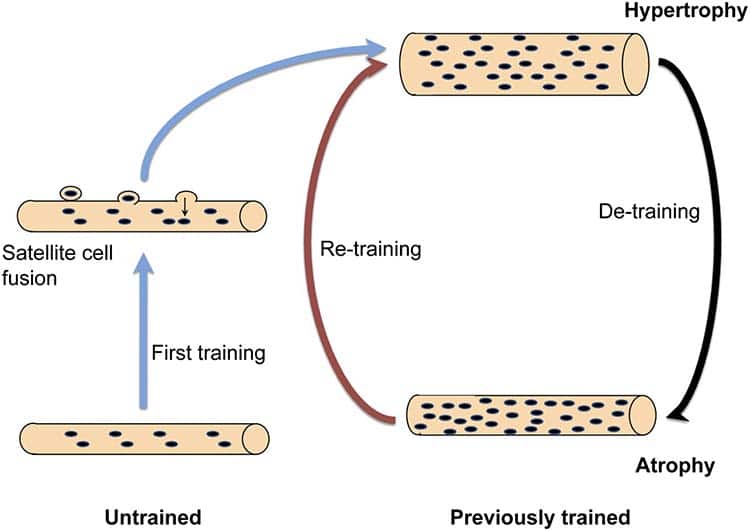
If you used to lift weights routinely way back when there may be good news for you, it’s much easier to re-build lost muscle than it is to build that muscle from scratch.
If you’ve ever heard of the phrase ‘muscle memory,’ it turns out that it does exist. The old school bodybuilders were onto something when they noticed this phenomenon occurring.
It turns out that the nuclei in the muscle (myonuclei) created during hypertrophy (muscle growth) is never lost, even though the muscle fibers decrease in size (atrophy) due to inactivity. Once you begin training again, the myonuclei can signal muscle growth much quicker than had you never trained before.10 11
A de-trainee could potentially fall under the category of beginner since they're often able to achieve the same results as a beginner would in respect to muscle gain and fat loss.
How To Calculate Your Keto Bulking Calorie Surplus
Now that I’ve outlined the different scenarios, you should have a good idea of where you might fall on the spectrum from beginner to an advanced trainee. The below recommendations will outline how much of a surplus you should generally be in to maximize muscle gain, but while minimizing the amount of fat gain.
All numbers are relative to theoretical caloric maintenance. 12
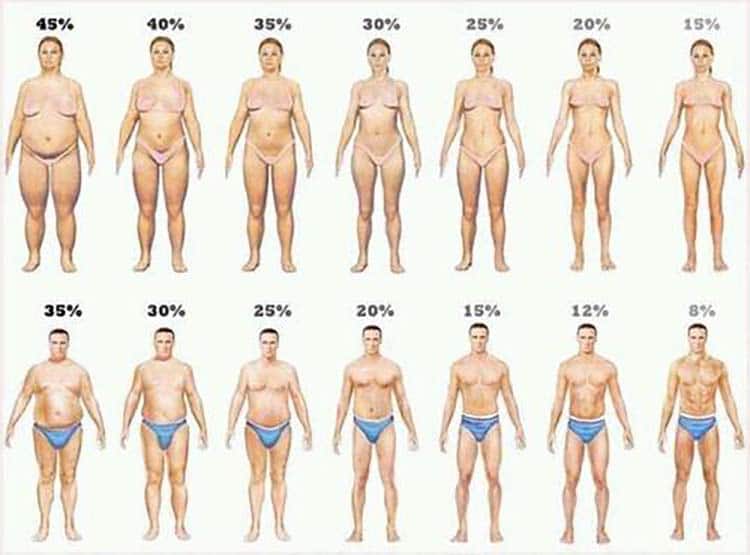
A more accurate body fat test such as a DEXA scan, bodpod, and other similar method should be utilized to determine body fat percentage. If you want to take a stab at guessing I've included a visual guide below for reference.
- Beginner – Male < 12% body fat | Female < 22% body fat – ~25% caloric surplus
- Intermediate – Male < 12% body fat | Female < 22% body fat – ~15-20% caloric surplus
- Advanced – Male < 12% body fat | Female < 22% body fat – ~10-15% caloric surplus
- Beginner – Advanced Male ~13-18% body fat | Female ~23-28% body fat – ~5-10% caloric surplus
If you want to make things even more straightforward, a good rule of thumb is to eat between 100 – 300 calories above maintenance. Beginners and detainees would stick more toward the higher end while intermediate and advanced will gravitate toward the 100 – 200 calorie surplus range.
You should expect to gain 1 – 4 pounds of weight on average per month. Again, beginners and detainees will want to stick with the higher range of ~4 pounds per month, while intermediate and advanced trainees should be closer to the ~2 pounds per month.
If you do not see the appropriate amount of weight gain, increase calories by an additional ~5-10% until you achieve the desired rate of gain.
How To Calculate Maintenance Calories On Keto
Maintenance calories are the number of calories needed to maintain your weight. While the number of calories will vary slightly day to day, our goal is to calculate what our average theoretical maintenance is to calculate our surplus.

There are three general methods I like to use to calculate maintenance calories:
- Use a formula
- Use a simple multiplier
- Food diary
Use a formula
There are a few popular formulas for calculating your maintenance calories. These calculators usually take into account your height, weight, lean mass, and activity level.
I won’t go into too much detail about the formula in this article. I’ll point you to our keto macro calculator, where it takes the average of the most popular formulas in an easy to use plug and play fashion and gives you a number.
Use a simple multiplier
A simple way to calculate maintenance calories for most people is to use the simple multiplier method. Take your body weight in pounds (lbs) and multiply it by 14 to 16.
If you are less active or a smaller individual, stick to 14. If you fall on the heavier or more active side, perhaps start with 16 as your multiplier. You’ll find that if you use the keto macro calculator and select maintain as your goal, that these numbers should be pretty close.
Food diary
Using the food diary method is the most time consuming, but it is the MOST accurate method compared to the previous two. If you have the patience or were previously tracking, then I would recommend this method over the previous ones mentioned.
A little caveat, if you HAVEN’T transitioned to a ketogenic diet yet, these numbers may be skewed. Water fluctuations within the first two weeks of adopting a ketogenic diet are normal but don’t give us consistent enough data to determine our maintenance calories. If you find yourself in this scenario, I would first get the ball rolling with your keto diet and start tracking starting on the third week after the dust settles.
To use the food diary method:
- Track body weight and calories every day for two weeks and average them out
- Determine average weight gained or lost
- Determine your maintenance calories based on weight gained or lost
- If your weight remained the same, then you’ve found your caloric maintenance
- If you lost weight, assuming you need a 500 calorie deficit per day to lose one pound per week, you could determine your maintenance by calculating how much of a deficit you were in.
(2,500 + .5 x 500 = 2,500 + 250 = 2,750 calories)
An additional example
Example: if you ate 2,500 calories per day on average and GAINED 0.5 pounds between the first and second week, then to calculate maintenance:(2,500 – .5 x 500 = 2,500 – 250 = 2,250 calories)
Whichever method, take your maintenance calories and add the appropriate surplus based on the appropriate percentage outlined in the previous section.
How To Calculate Your Keto Bulking Macros
To calculate our bulking macros on keto is pretty straight forward. After all, we are limiting or eliminating carbohydrates from the equation, thus making protein and fat the only variables we have to worry about it.
Once calories are determined and carbs limited (to whatever number you are sticking with, but generally 0 to 50 net carbohydrates for most), our next step is to determine protein intake. The amount of protein needed to optimize muscle gain is a highly debated topic. Still, there’s one thing that’s certain; protein is the most essential macronutrient when it comes to repairing and building muscle. 13
How Much Protein To Bulk On Keto

By nature, a ketogenic diet is protein sparing through a variety of mechanisms, making it an excellent diet for those wishing to lose fat while retaining as much lean mass as possible. Combine a diet that is protein sparing with a caloric surplus, and you may be wondering just how much protein you may need to build muscle optimally.
To make this as simple as possible, the recommendation for protein while bulking on keto will default to 1 gram of protein per pound of bodyweight. 14 However, if you prefer more protein due to preference or satiety purposes 15, you may increase this number to 1.6 grams, but per pound of LEAN BODY MASS, not weight.
There is a reason to believe that higher intakes of protein may be optimal for muscle gain and body recomposition1617, but 1 gram per pound of body weight is a fast and straightforward general rule. Whether you prefer more or want to experiment with higher intakes is left for you to decide.
If you are unsure of your body fat percentage, and do not have access to get it accurately tested, utilize the visual chart below to get a rough estimate:

How Much Fat To Bulk On Keto
Since we calculated our caloric surplus, limited our carbs, and picked a protein level… the only macronutrient left is fat.
This macronutrient is the easiest to calculate. By default, all the remaining calories after carbohydrates and protein will come from fat.
Example: A 200lb male
- 3,000 calories
- 50g of carbohydrates x 4 calories per gram = 200 calories
- 200g of protein x 4 calories per gram = 800 calories
- 200 + 800 = 1,000 calories from carbohydrates and protein leaving 2,000 calories from fat
- Fat has 9 calories per gram (2,000 / 9 = 222 grams of fat)
Bill’s calories and macros for his keto bulk are 3,000 calories, 200 grams of protein 222 grams of fat, and 50 grams of carbohydrates.
How Frequent To Eat On Your Keto Bulk
It seems as if the entire ketogenic community is doing some version of intermittent fasting (IF), whether it’s 16:8 or one meal a day (OMAD). While you can still gain muscle using an intermittent fasting eating schedule, it may not be the most optimal. However, if you prefer to eat this way due to adherence or preference, you can still make progress. 18
What’s most important is your total calories and total protein intake, but if you wish to maximize your gains further, the rest of this section is for you.If you’re looking to make the MOST gains possible during your keto bulk, and willing to do everything necessary to maximize muscle gain, I suggest a meal frequency of approximately three to five meals per day. Spreading out your protein in three to five meals will help maximize muscle building for reasons I will outline below.
You see, there are a minimum AND a maximum amount of protein per meal that helps to stimulate muscle protein synthesis (MPS). Eating any more protein than this amount will not stimulate MPS any higher, and not eating enough protein won't maximally stimulate MPS.
Muscle protein synthesis is the process of building muscle protein, the opposite of muscle protein breakdown (MPB).
Both MPS and MPB are happing all the time, and it is the sum of these two processes that determine your net balance. If muscle protein synthesis exceeds muscle protein breakdown, your muscles will grow.
You may be wondering, why can’t you consistently eat boluses of protein to stimulate muscle protein synthesis? Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) experiences a ‘muscle full effect.’ MPS can be stimulated for a short period, after which a refractory period ensues and will not respond to any more amino acids.
MPS peaks 90 to 120 minutes post-meal, after which MPS returns rapidly to baseline.1920
For most individuals, 20 grams of protein in one sitting is enough to stimulate protein synthesis while going up further to 40 grams of protein may yield you a 10 – 20% increase.2122
Smaller individuals may get by with 20 grams, while larger individuals should aim closer to the 40 grams per meal. To be more specific, 0.40 g/kg/meal is what you should aim for to maximize MPS response.
Keto Bodybuilding Supplements

Supplements are the last 5 – 10% that can potentially take your training and nutrition to the next level. Consider supplements only after you have all the other big rocks in place.
Supplements are NOT REQUIRED to gain muscle, and fine-tuning your nutritional and training approach will yield you better results than any supplement.Remember, they are called supplements for a reason. They are meant to supplement your diet and training, not make up for it. Subpar diet and exercise couldn’t be made up for with all the supplements in the world. 23
Not all supplements are created equal. The truth is, most supplements on the market will offer very little to no benefit. When considering if you should take a supplement, ask the following:
- Is it worth the cost?
- How effective is it?
- Are there any adverse side effects?
While cost is subjective, the other two are not. Based on the criteria outlined above, these are the supplements I would recommend or are worth considering.
Highly recommended supplements for your keto bulk
Protein powder
Think of protein powder as a powdered version of a chicken breast or egg whites. There is nothing magical about protein powder that you couldn’t get from eating whole foods. However, protein powder is a convenient and effective way to reach your daily protein requirements when you don’t have the time or the appetite to eat solid food.
Creatine
Creatine is the most studied and effective supplement shown to increase performance and muscle size.24 Additionally, creatine has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective properties.25
Any brand of creatine with the main ingredient “creapure” is fine. ~5g of creatine per day, any time of the day is recommended.
Check prices for creatine here.
Caffeine
Evidence supports the use of caffeine for increasing strength, prolonging fatigue, cognitive function, and much more.26
If looking to maximize strength and performance, doses between 3-6mg/kg are what’s shown to be effective. You'll commonly find this amount in many pre-workout supplements.
The more frequent you use caffeine, the less effective it becomes. Essentially, over time, your body begins to build a tolerance to caffeine.
To maintain the effectiveness of caffeine, reserve it for your hardest workouts, or cycle off of caffeine periodically.Check the prices of caffeine here.
Supplements worth considering for your keto bulk
Multivitamin
While it’s recommended to try and fill your nutrition needs from unprocessed whole foods, It’s not always easy to fill your micronutrient requirements from diet alone, especially for athletes.
Think of a multivitamin as a micronutrient insurance policy. However, not all multivitamins are created equal. Some multivitamins include forms of vitamins that are less bioavailable. Subpar types of particular vitamins make the vitamin less effective, if at all.
Fish oil (Essential Fatty Acids)
The typical North American diet is deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. Deficiency in Omega 3 fatty acids may lead to increased risk of cardiovascular disease, fatigue, poor memory, depression, and other negative symptoms. 27
A great way to increase your intake of EFA’s in your diet is by consuming fatty fish, grass-fed meats, and pasture-raised eggs. Supplementation wise, certain studies suggest that you may benefit from increased absorption with krill oil over fish oil, though not conclusive.
Around 2g of combined EPA and DHA per day is recommended.
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is considered an herbal adaptogen, a natural substance considered to help the body adapt to stress. Further research suggests it may improve strength performance and even testosterone levels.28
When supplementing with ashwagandha, choose one with the KSM-66 stand of ashwagandha, the most studied in the literature. An average dose of ashwagandha is between 500mg to 1,000mg and suggested to be taken either post-exercise or before bed.
Check current prices for ashwagandha here.
Best Way To Gain Muscle On Keto?
I’ve gone over how to set up your keto bulk to maximize muscle gain while limiting fat gain, which is inevitable when eating in a surplus. Specific individuals may achieve body recomposition, which is simultaneously gaining muscle while losing fat, but usually only occurs under a variety of circumstances.
If you’re serious about taking up a keto diet and bodybuilding, I’d suggest giving my other article a read. In my keto diet bodybuilding guide, I go over all the different aspects of setting up your diet, training, nutrition, and other important, but often overlooked aspects of gaining muscle in an 8,000+ word article.
The Takeaway
Muscle can effectively be built on a ketogenic diet as it can on a standard diet based on carbohydrates. Many of the same principles apply whether you’re keto or not. That is, the most critical factors are sufficient energy intake (calories) and progressive overload (resistance training).
The most important thing you can do is to pay close attention to your biofeedback and make adjustments as necessary to both your training and nutrition to ensure continued progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it hard to bulk on keto?
When you gain muscle on keto it's both attainable and sustainable. If you make small tweaks to traditional keto then it's definitely possible to bulk easily.
Can I grow muscle on keto?
If you keep your body in ketosis it can help gain muscle and will lead to a decrease in workout performance initially. However, once your body gets used to the diet, you'll return to your previous workout performance levels.
How do I clean my bulk on keto?
It's quite simple to do a clean bulk while you're on keto. Simply pick foods that have high amounts of protein in them and then apply keto principles to make up the calories. Following the keto principles will ensure that you eat enough fat and stay away from the carbs while you're on the bulk.