What's weird is that before starting a ketogenic diet, I was more of a sweet than savory type, but after going keto, that completely reversed. Now, it's like I crave salt like there's no tomorrow.
Naturally, I questioned why this was, and through the years this is what I've learned,
Why are you craving salt on keto? The most often causes of craving salt when first starting keto is due to dehydration, an electrolyte imbalance, less insulin, and the stress your body is undergoing when transitioning into a ketogenic diet.
In this article, I'll explain what salt does in your body, why you're having intensive cravings, how much you should be eating, the benefits, and even the best salts to use.

Table of Contents
Why You Crave Salt On Keto
There are various reasons why people start to crave more salt when switching to a ketogenic diet. Often, they are usually a result of the reasons I'm about to list for you below.
Dehydration
High carbohydrate consumption has caused your body to retain water and salt up until now. When you eliminate carbohydrates from the diet, you begin to expel pounds of water (yes, pounds).
On average, your body stores ~500 grams of carbohydrates (glycogen). With every gram of glycogen your body stores, an additional three grams of water is stored with it.
That's 1,500 grams (1.5 kg or 3.3 lbs) of water that is stored just with the carbohydrates in your body.
When you eliminate carbohydrates from your diet, the stored carbohydrates are eventually used for energy, and the water is expelled, primarily through urination.
- Read: Why You Pee So Much When Starting Keto
Electrolyte Imbalance
Everything you ate previous to starting a ketogenic diet was probably salted up the wazoo.
Now, chances are none of your food is pre-salted, and because you've eliminated a majority of carbohydrates when starting keto, your body is expelling water…
… and with that water, electrolytes are being lost.
It's the same reason athletes need sports drinks because when they sweat, they also lose electrolytes.
Sports drinks are fortified with sodium and potassium to help replenish sodium and potassium lost through sweat and urination.
Electrolyte are important, especially when first starting a ketogenic diet, most notably sodium and potassium.
Electrolytes I recommend:
Low Insulin
You may think of insulin as the regulator of blood sugar, but insulin also helps the body retain sodium. Without insulin, the kidneys can filter it into the urine at a much quicker rate.
In a 2012 study, this was demonstrated by Type 1 diabetics who do not produce insulin, thus have low insulin levels. These individuals experienced high levels of salt loss through urination. 1
This study demonstrated the opposite effect; they found when given insulin, people's sodium concentration in their urine was reduced, meaning more sodium retention. 2
Low carbohydrates = low insulin and lowered insulin lead to increased excretion of sodium via the kidneys.
Caffeine

Are you a coffee or tea drinker? Many people following a ketogenic diet seem to increase their caffeine intake with keto or bulletproof coffees exponentially, and I get it… they are delicious.
One study found that one cup of coffee (about ~90mg of caffeine) led to 437 mg of extra sodium loss out the urine. When participants consumed around four cups of coffee, there was around a 1,200mg of additional loss of sodium from the urine. 3
If you're ridding your body of salt with extra caffeine, your body may be giving you a sign to replenish it.
Stress
Changing diets, such as switching from a carbohydrate-based diet to a ketogenic diet, can be a lot of stress on a person's body.
Craving salt is one way your body may be trying to deal with the stress your body is undergoing.
Cortisol, also known as the “stress hormone,” is released by the adrenal glands as a response to stress. Some research indicates that people with higher levels of sodium release lower levels of cortisol. 4
A craving for salt may be your body trying to deal with this stressful transition.
A deficiency
You might be asking what deficiency causes you to crave salt? And that's an easy one, salt!
Duh!
Think of your salt cravings as a built-in “thermostat” that helps you get in the right amount of salt.
The reason you're craving salt is that your body's “salt thermostat” is set at a certain level, and you're currently below it. Your body responds by increasing cravings for salt to bring your levels back up to where it believes to be sufficient.
Your hypothalamus produces hormones that dictate your inherent needs.
Hard-wired?
Some scientists believe that our salt cravings go back to prehistoric times, which makes sense.
Salt was not as available as it is today. The though is that our brain developed a “reward system” that encourages us to seek out salt when possible; otherwise, we'd die.
And this makes sense because certain animals in the wild go out of their way to seek out salt licks. https://www.ncpedia.org/salt-licks
Why You Need So Much Salt On Keto
You may be wondering, do you need more salt on keto? Yes, you do need more salt on keto.
While following a ketogenic diet, your needs may be more significant than with a carbohydrate-based diet.
Since carbohydrates help store water in our body, and we're severely limiting them from our diet, we don't have as big of a reservoir for holding water.
Therefore, the majority of the burden comes down to the intake of sodium to ensure proper bodily functions and water retention.
What Happens When You Don't Eat Enough Salt
In today's society, we're scare mongered into believing high salt intake will lead to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and hypertension In everyone.
When you start cutting sodium to less than 3000mg/day, renin, angiotensin II, and aldosterone begin to skyrocket. 5
Increased stress
The stress hormones noradrenaline and adrenaline are activated when we restrict salt intake.
Higher risk of death or hospitalization
Restricting sodium to less than 2,500 mg per day was associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality or hospitalization, compared to those who did not restrict sodium. 6 7
Decreased sodium also could lead to:
- Increased cholesterol and triglycerides 8
- Insulin resistance 9 10
- Hyponatremia 11
How Much Salt / Sodium On Keto?
There's a difference between how much salt we need for basic survival and the necessary salt intake to thrive.How much salt you need is individual, your body controls your salt intake, and that's why someone may crave salt more or less than another despite eating the same amount of salt.
Your body has mechanisms in place to control these cravings.
As of 2016, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reduced their Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) of sodium from 2,400 to 2,300 mg/day.
Based on what I've laid out for you in the previous section, you can see how a deficiency in sodium may lead to a whole host of adverse effects.
Why do you need so much salt on keto?
Combine a low sodium intake with a low carbohydrate diet, and you have a recipe for disaster.
Are you craving salt and tired? This may be why you're feeling exhausted on a ketogenic diet or suffering from all the signs and symptoms of the “keto flu.”
You need more salt because:
- You have fewer carbohydrates helping you store water
- Producing less insulin due to lowered carbohydrates, which means more sodium excretion
- Eating less salt in your diet due to eating more whole-foods
So do you need more salt on keto? Yes, your need for salt will increase on a ketogenic diet; that's why you may experiencing these salt cravings.
I'd recommend at least two teaspoons of salt a day (~4,000mg) when following a ketogenic diet. This much salt can come from foods you enjoy, like salted butter and bacon, etc., but it's also essential to salt your foods liberally and to taste.Salts I recommend:
Keto, salt, and exercise
If you're a very active individual or athlete who sweats profusely, which I found out the hard way, then an additional ~ one teaspoon pre-workout may help keep you hydrated and even improve exercise performance.
Taking salt before exercise can help:
- Decrease thirst
- Increase exercise capacity
- Improve performance
- Improve muscle gains
- Decrease the risk of hyponatremia
- Lower risk of iodine deficiency
- Improve kidney function
Salt sensitive vs. salt resistant
Salt sensitive individuals are the ones who respond poorly to high salt intakes.
Salt resistant individuals don't respond very much in response to a diet high in salt. If you have healthy kidneys, they are capable of excreting excess salt very efficiently.
About a third of people with high blood pressure are actually salt resistant. 12 About 5% of these individuals have reverse salt sensitivity, meaning, their blood pressure improves when they increase their salt intake. 13 Increases in age and weight make you more susceptible to being salt sensitive.
Additionally, here are a few more individuals who may be more salt-sensitive:
- Women
- African Americans
- Diabetics
- Those suffering from chronic kidney disease
Is Salt and Sodium The Same Thing?
So what does salt exactly do in our bodies? Why is salt so important?
First, let's distinguish a difference between salt and sodium.
Salt and sodium are not the same things.
We get sodium from salt, but salt is not sodium.Instead, salt is sodium chloride, which is table salt. Sodium chloride is only 40% sodium and 60% chloride.
Take my favorite salt, Redmond Real Salt, as an example:
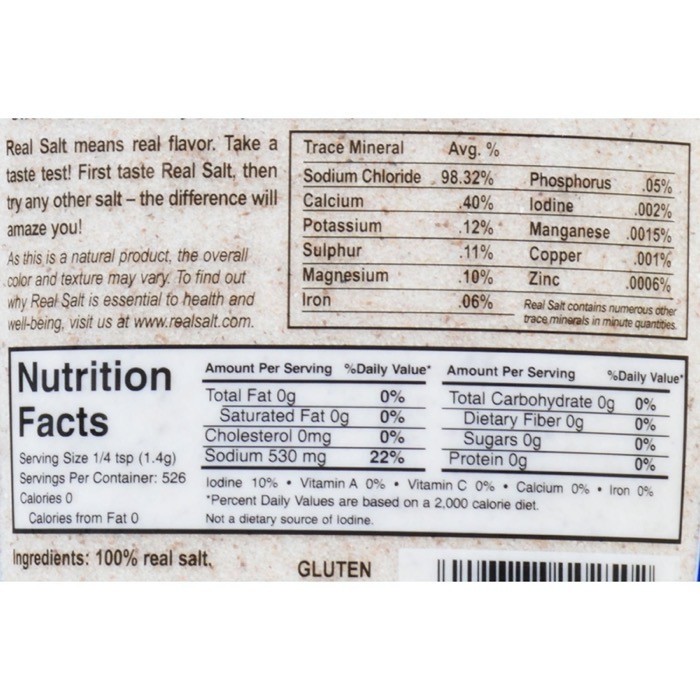
As you can see, 1/4 tsp (1.4g) serving has only 530mg of sodium and not 1.4g of sodium.
What Does Salt Do In Our Body?
Now that we know the difference between salt and sodium, why is it so important?
Salt, our primary source of sodium, is a mineral and electrolyte that does some of the following:
- It helps maintain the right amount of fluid in and around our cells.
- It helps muscles work efficiently.
- It helps with nerve signaling throughout your body.
And that's just the tip of the iceberg.
Sodium is ESSENTIAL for life!
What Are Symptoms Of Low Sodium and Salt On Keto?
There are many common symptoms associated with low blood sodium; they include:
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Muscle cramps
Do these sound familiar? It should because these same signs and symptoms happen to people who suffer from the “keto flu.”
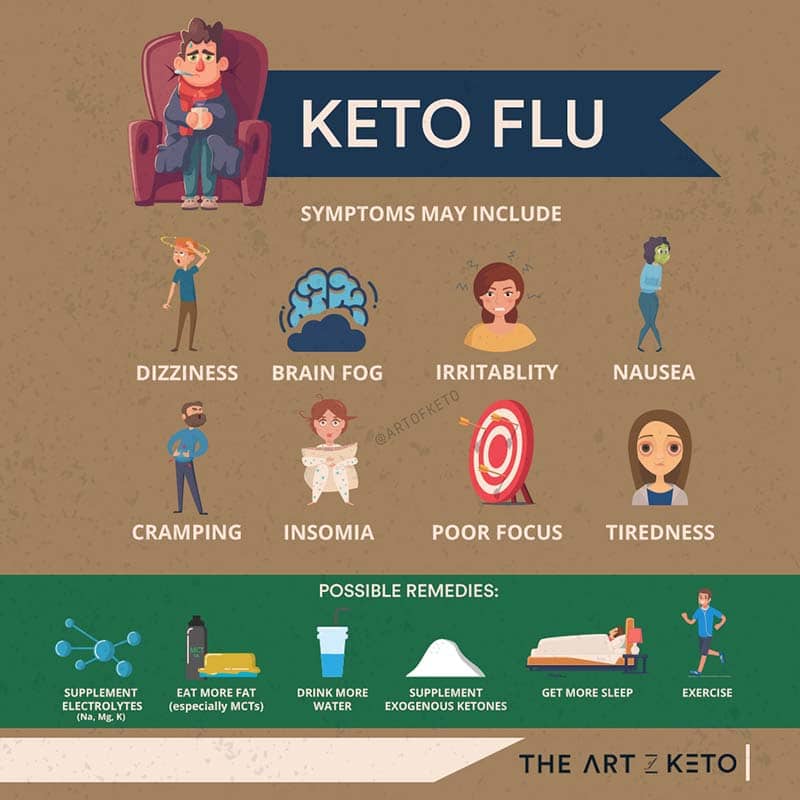
Most people suffering from these signs and symptoms think that they mean you're entering ketosis or expected to happen. Still, from my experience, it means you're dehydrated and have an electrolyte imbalance.
Other symptoms that may indicate a greater need for salt:
- Cold extremities
- Dark urine
- Decreased urine output
- Dizziness and hypotension (occurs after rising from a seated position)
- Thirst and salt cravings
- Constipation
- The “shakes”
- Heart palpitations
What To Eat When Craving Salt?
There are no special foods you “should” eat when it comes to your salt cravings; this may be just your body's way of telling you it needs salt.
I recommend people salt their foods to taste, and that is often enough to solve the salt cravings.
Think about it.
If you put TOO MUCH salt, you WILL know, because now your food just became inedible.
Which Salt To Use For Keto?
It doesn't matter which salt you use since sodium is sodium.
However, some salts do offer additional minerals and arguably taste a lot better.
If you can, use unprocessed salts such as:
- Redmond real salt
- Celtic sea salt
- Table salt (if budget is of concern)
The Takeaway
If you're craving salt on keto, it's because your body may be signaling you that it needs sodium.
Due to the low-carbohydrate nature of a ketogenic diet, less sodium and water are retained, thus increasing the need for salt in the diet.
For athletes or active individuals who excessively sweat, additional salt may be required and even suggested to help improve performance.
“You could live the rest of your life without eating another granule of sugar, but you can't stay alive for very long without salt.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What to eat on keto when craving salt?
When you have an intense craving for salts, there are quite a few things that you can enjoy eating while on keto. Some of them include canned sardines, olives, zucchini sticks, and macadamia nuts!
Why do you need so much salt on keto?
When the body loses electrolytes as it does while on the keto diet, your sodium levels will go down. To regulate them back to a normal level, it's important to eat salty foods.
How much salt should I have on keto?
When you're on the keto diet, ideally you'll need to consume between 4000-7000 mg of sodium to ensure that you don't run on an electrolyte deficiency.
