One thing I struggled with when starting a ketogenic diet was achieving a pump, the feeling of my muscles swelling and about to burst through my skin.
While it may be harder to achieve a pump on keto or low carb, here are a few tips someone can utilize:
- Consume an adequate amount of electrolytes, mainly sodium.
- Stay well-hydrated.
- Strategically use carbs such as a targeted ketogenic diet or cyclical ketogenic diet.
I mean, there's nothing better than feeling your shirtsleeves stretch during or after a brutal workout, even if it is just a boost for my ego, but how do we get that same pump we had on a carbohydrate-based diet on keto?
In this article, I'll go over exactly how to get that pump back while following a ketogenic diet, what causes it, the best pre-workout to use for a better pump, and much more.

Table of Contents
How To Get That Pump Back On Keto
So you started a ketogenic diet, and now you're feeling flat in the gym. You may feel that you simply don't have that same muscle swelling you once had on a carbohydrate-based diet, and you're not wrong.
But that doesn't mean you can't achieve that superhero feeling you once had after an intense workout, especially an arm day.
Here are some tips to get you headed in the right direction.
Increase electrolytes
When you first started a ketogenic diet, you may have noticed that your weight dropped rapidly during the first week or two.
While some of the weight you lost may have been fat, a more significant proportion of it was water weight and food volume.
The average adult stores ~500 grams of carbohydrates in the form of glycogen, located in both your muscles and your liver.
For every gram of carbohydrate your body stores, the body will store 3 grams of water.
In the beginning, when you're restricting carbohydrates, your body begins to burn through your stored glycogen. With no carbohydrates to bind to, the extra water is flushed from your body, usually through urination.
This may be why, if you noticed, that you pee more frequently when first starting keto.
But, as your body expels this water, it will also flush out electrolytes with it, especially sodium and potassium.
The loss of electrolytes is usually exacerbated even further because you may be eating less sodium-filled foods in your diet now that you're keto.
You can usually combat this by making sure you take in an adequate amount of salt by making sure to salt your foods but also supplementing with additional salts and electrolytes if you work out and sweat regularly.I recommend an excellent electrolyte supplement that has a sufficient amount of potassium, which most don't.
Being deficient in electrolytes will do more than just keep you from getting a pump; it can make you weaker, and you may begin to experience muscle cramps.
Sodium and potassium are important minerals that help your body maintain fluid balance, so you must get in a sufficient amount. 1
I'd recommend at least 4,000mg – 6,000mg sodium and potassium each per day MINIMUM.
Here is one that I would recommend:
Stay hydrated
Playing off the previous recommendation, you have to make sure you're well hydrated.
Along with electrolytes, you have to maintain adequate hydration to get a pump in the gym. Upwards of 60% of your body is made of water, but your muscles are made up of more than 70 percent water. 2 3
In short, drink enough fluid that your urine isn't super yellow, and not too much to where it's clear like water. Use the chart below as a reference as to where you want your urine color to be generally.
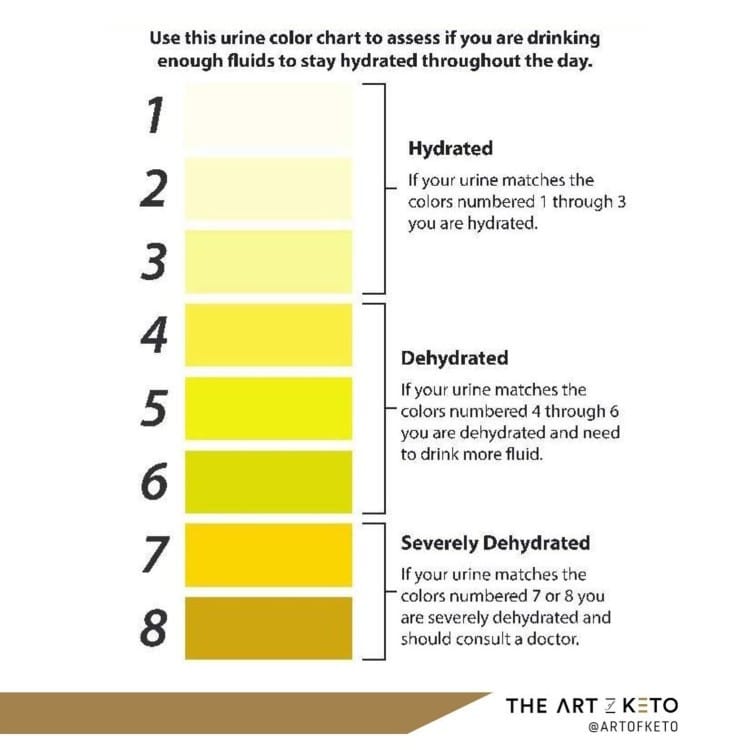
This, along with the previous step (electrolytes), will solve most of your issues when it comes to getting a pump in the gym.
Another trick I like to use is to take a teaspoon of salt with my pre-workout or dilute salt into a big jug of water and sip it throughout the day. This way, you get extra minerals and sodium while staying hydrated.

Specialized Ketogenic Diets
There's more than one way to do keto, especially if you're an active individual or an athlete.
In general, there are three different kinds of ketogenic diets:
- Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD)
- Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD)
- Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD)
Standard Ketogenic Diet
The standard ketogenic diet is most likely what you're doing now, very low to no carbohydrates seven days a week, somewhere in the ballpark of 20 to 50 grams of net carbs per day.
Targeted Ketogenic Diet
A targeted ketogenic diet is how it sounds in that you target carbohydrates around your workouts.
Most people following a ketogenic diet consume somewhere between 5-50 grams of carbs pre and post-workout while still being able to stay in ketosis.
- Read more about a TKD: Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD)
Cyclical Ketogenic Diet
Cyclical ketogenic diets are the most complex of the three. During a cyclical ketogenic diet, you'll be mixing days of a standard ketogenic diet with a couple of high-carbohydrate days.
Usually, people will do a 5/2 or a 6/1 ratio, so a 5-day SKD then 2-day carb-up or 6-day SKD then 1-day carb-up.
There's typically a specific workout regimen that would go along with implementing a CKD optimally, but it's not for the faint of heart.
- Read more about a CKD: Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) Carb Ups And Keto
By using a TKD or CKD, you're filling your muscles with a little extra glycogen that will help boost both your performance and pumps in the gym.
Why Does Salt Give You A Pump?
First, I should clarify that it's technically not salt that helps with a pump, it's the sodium. Salt is technically a 1:1 mix of both sodium and chloride.
That said, one of the responsibilities of sodium in the body is to help regulate blood volume and blood pressure.
During a workout, we know that the primary reason we get a pump is due to increased blood volume to the working muscle.
A low sodium intake translates into lower blood volume, and lower blood volume equates to little or non-existent pumps in the gym.
If you want a pump in the gym, then make sure you're getting an adequate amount of salt/sodium in your diet.
Unless you have a specific condition that prevents you from increasing your salt intake, your body is well-equipped to process any excess.
For a good read on salt and all its health-promoting benefits, I'd recommend giving The Salt Fix a read.
What Is A Muscle Pump?
You may be wondering what exactly is going on during a muscle pump.
When you lift weights and contract a muscle repeatedly, blood and water get diverted to the working muscle to support the increased metabolic needs.
As the muscle swells, the surrounding veins are constricted, resulting in more blood becoming trapped in that specific muscle group.
It's like if you were to turn on the hose and fold or tie a knot somewhere in the line. The pressure would accumulate, and the water would get trapped at a certain point, thus expanding the hose at the point of constriction.
Do Carbs Give You A Better Pump
People may confuse carbs with giving them a better pump because they don't give a ketogenic diet enough time to work out the kinks. After all, switching to a ketogenic is a significant shift and requires a bit of a learning curve.
As I've alluded to earlier, carbs hold water, and your muscles are made up of mostly water.
However, while glycogen may be impaired during the beginning of a ketogenic diet, there seems to be no significant difference in muscle glycogen levels once you become fat-adapted. 4
Given enough time, your muscle glycogen stores will begin to re-fill, even without carbohydrates in the diet.
So while carbs give you a better pump “temporarily,” you should be able to experience these same effects by ensuring you have an adequate intake of electrolytes, water, and good ole' time to become “keto-adapted.”
Building Muscle On A Keto Diet
People always ask me, what's the best way to gain muscle on keto? And I usually respond “the same way you build muscle when not on a ketogenic diet.”
This means:
- Adequate training stimulus
- Sufficient nutrition
- Proper recovery
The same principles that applied on a carbohydrate-based diet apply when you're on a ketogenic diet.
If you want to learn more about how to bulk on keto without getting fat or how to implement bodybuilding principles, then give the two articles below a read.
What's The Best Preworkout To Get A Pump On Keto?
Now that we've gone over how you don't have to live a life of “flatness” during your workout, what else can you do to help get a pump on keto?
If you've taken care of the above points, there are additional products and pre-workouts you can take to help increase blood flow, blood volume, and get some sick pumps in the gym.
Creatine
There's often this misconception that creatine makes you bloated and hold water.
Ok, it's not completely untrue, creatine DOES make you hold water, but it does so INSIDE the muscle. 5
Since muscles are made up of over 70 percent water, by saturating your muscle creatine stores, you'll increase intramuscular water retention.
Meaning, you'll have bigger, rounder, and fuller muscles while taking creatine.
Creatine is also the MOST well-studied performance-enhancing supplement and very cheap at that.
I'd recommend supplementing with 5g of the monohydrate version per day, and don't bother with the “loading phase.”
L-Citrulline
Besides creatine, L-Citruline is another supplement that has a reasonable amount of scientific support. You may even find them in the current pre-workout you're using. 6 7 8
Unfortunately, though, MOST companies underdose L-CItruline in their pre-workout formulation. Either that or you don't know how much is in it due to their “proprietary blends.”
L-Citrulline can increase blood vessel diameter (vasodilation), allowing higher blood flow to your muscles.
And we all know increased blood volume and blood flow equals greater pumps.
According to the studies, a dose of 4-10 grams of l-citrulline has shown to be an effective dose.
Pre-workout
If you just want to take a pre-workout instead of buying L-Citruline separately, remember that most of them are underdosed.
Here are a few of the more reputable companies I would recommend that have clinically effective doses of the ingredients in their products.
The Takeaway
We all love that feeling of our shirts hugging our sleeves and our chest, but many people starting a ketogenic diet often lose this sensation due to being misinformed.
Achieving a pump on keto is all about understanding WHY you're not getting a pump anymore, and it's not because you don't have carbs in the diet.
Make sure you're getting in an adequate amount of electrolytes and water, followed by allowing enough time to keto-adapt, and you'll have all the same pumps you used to get following a carbohydrate-based diet.
If you want to step it up a little further, adding in some supplements like creatine or l-citrulline will help fill your muscles with water and increase blood flow, allowing more muscle growth and giving you a better pump.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I gain muscle while on keto?
It's definitely possible for your body to gain muscle while it's in ketosis. However, if you're just entering into ketosis it might decrease your workout performance.
How to gain muscle mass on keto diet?
To gain muscle mass on the keto diet its important to lift weights regularly. If you're lifting weights regularly, you'll need to consume enough calories and make sure you eat the right amount of protein.
Can I gain muscle without carbs?
It's definitely possible to build muscle while you're on a low carb diet. However, you will feel a definite reduction in your workout performance due to the lack of glucose.
